
A partial knee replacement is surgery to replace only one part of a damaged knee. It can replace either the inside (medial) part, the outside (lateral) part, or the kneecap part of the knee.
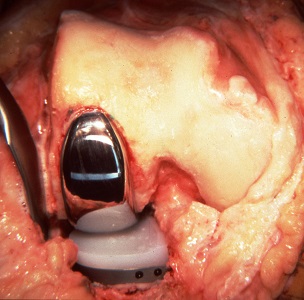
Partial knee replacement surgery removes damaged tissue and bone in the knee joint. The areas are replaced with a man-made implant, called a prosthetic.
Before surgery, you will be given medicine that blocks pain (anesthesia). You will have one of two anesthesia types:
The surgeon will make a cut over your knee. This cut is about 3 to 5 inches long.
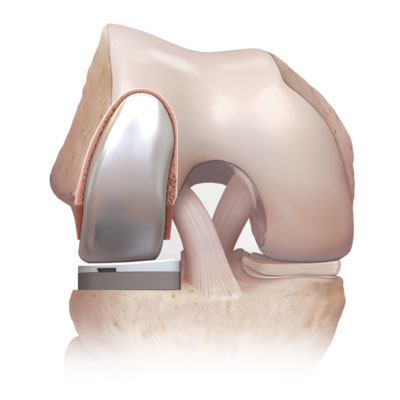
The most common reason to have a knee joint replaced is to ease severe arthritis pain. Your doctor may suggest knee joint replacement if: You can't sleep through the night because of knee pain. Your knee pain prevents you from doing daily activities. Your knee pain has not gotten better with other treatments. You will need to understand what surgery and recovery will be like. Partial knee arthroplasty may be a good choice if you have arthritis in only one side or part of the knee and: You are older, thin, and not very active. You do not have very bad arthritis on the other side of the knee or under the kneecap. You have only minor deformity in the knee. You have good range of motion in your knee. The ligaments in your knee are stable. However, most people with knee arthritis have a surgery called a total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Knee replacement is most often done in people age 60 and older.
Always tell your health care provider what drugs you are taking, including herbs, supplements, and medicines bought without a prescription. During the 2 weeks before your surgery: Prepare your home.
On the day of your surgery: You may be told not to drink or eat anything for 6 to 12 hours before the procedure. Take the medicines your doctor told you to take with a sip of water. Your provider will tell you when to arrive at the hospital.
You may need to stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days. Most people are able to go home the day after surgery. You can put your full weight on your knee right away. After you return home, you should try to do as much as you can. This includes going to the bathroom or taking walks in the hallways with help. You will also need physical therapy to improve range of motion and strengthen the muscles around the knee.
Most people recover quickly and have much less pain than they did before surgery. People who have a partial knee replacement recover faster than those who have a total knee replacement. Many people are able to walk without a cane or walker within 3 to 4 weeks after surgery. You will need physical therapy for 4 to 6 months. Most forms of exercise are OK after surgery, including walking, swimming, tennis, golf, and biking. However, you should avoid high-impact activities such as jogging.